The senescent chondrocytes were distributed in the central zone whereapoptotic morphological characteristics obviously appeared, such as pyknosis, karyorrhexis.
气 软
软 中央带多见衰老的软
中央带多见衰老的软 细
细 ,并见明显核固缩、核碎裂等细
,并见明显核固缩、核碎裂等细 凋亡形态学特征。
凋亡形态学特征。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
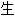 理学篇
理学篇 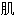



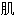

 关节炎
关节炎  关节炎
关节炎 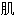

 关节炎
关节炎  关节炎
关节炎  关节炎
关节炎 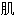

In healthy people, chondrocytes maintain a delicate balance between breaking down old cartilage—called catabolic activity, and producing new cartilage—called anabolic activity, through the use of both degradative enzymes and synthetic enzymes.
在健康的机体内,软 细胞在分解老化的软
细胞在分解老化的软 (分解作用)和
(分解作用)和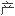
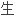 新的软
新的软 (合成作用)之间通过分解酶和合成酶来保持精细平衡。
(合成作用)之间通过分解酶和合成酶来保持精细平衡。
 关节炎
关节炎  关节炎
关节炎 Importantly, mutations in cartilage matrix genes such as COL2A1, COL9A3, COL11A2 and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), which are produced by articular chondrocytes, cause chondrodysplasia with early-onset OA.
重要的是,软 基质基因如COL2A1、COL9A3、COL11A2和软
基质基因如COL2A1、COL9A3、COL11A2和软 寡聚基质蛋白(COMP)的突变,这些基因由关节软
寡聚基质蛋白(COMP)的突变,这些基因由关节软 细胞
细胞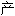
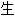 ,会导致软
,会导致软 发育不良并伴早期发病的
发育不良并伴早期发病的 关节炎。
关节炎。
 关节炎
关节炎 How articular chondrocytes, that primarily rely on glycolysis in low oxygen homoeostatic conditions, respond to joint damage and adapt to microenvironmental changes in articular cartilage is an important yet poorly understood question.
关节软 细胞主要依赖
细胞主要依赖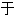 低氧稳态条件下的糖酵解,它们如何响应关节损伤并适应关节软
低氧稳态条件下的糖酵解,它们如何响应关节损伤并适应关节软 微环境的变化,是一个非常重要但尚不完全理解的问题。
微环境的变化,是一个非常重要但尚不完全理解的问题。
MSCs differentiate into adipocytes, osteocytes, chondrocytes, tenocytes, marrow stromal cells, muscle, and perhaps neuronal cells and are being used in early clinical trials to enhance bone marrow grafting and to suppress graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic bone marrow transplants.
MSCs分化成脂肪细胞, 细胞,软
细胞,软 细胞,
细胞, 腱细胞,
腱细胞, 髓基质细胞,
髓基质细胞, 肉和神经细胞,并用
肉和神经细胞,并用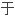 早期临床试验,以增强
早期临床试验,以增强 髓移植和抑制同种异体
髓移植和抑制同种异体 髓移植中的移植物抗宿主病。
髓移植中的移植物抗宿主病。